Introduction
1. What is Client-side AI?
Client-side AI (or In-browser AI) allows us to run artificial intelligence models directly on the user’s browser without sending data to a central server (Server/Backend).
- Privacy First: Input data never leaves the user’s device.
- Zero Server Cost: Utilizes the user’s hardware resources (CPU/GPU) instead of expensive cloud servers.
- Offline Capable: Once the model is loaded, the application can function even without an internet connection.
2. How it works
- Leveraging WebGPU: A modern graphics API that gives the browser direct access to the computer’s GPU for high-performance parallel computing.
- WebAssembly (WASM): Enables code to run at near-native speed in the web environment.
- Instead of calling APIs from OpenAI or Gemini Cloud, we fetch the model weights to the browser cache and perform Inference locally.
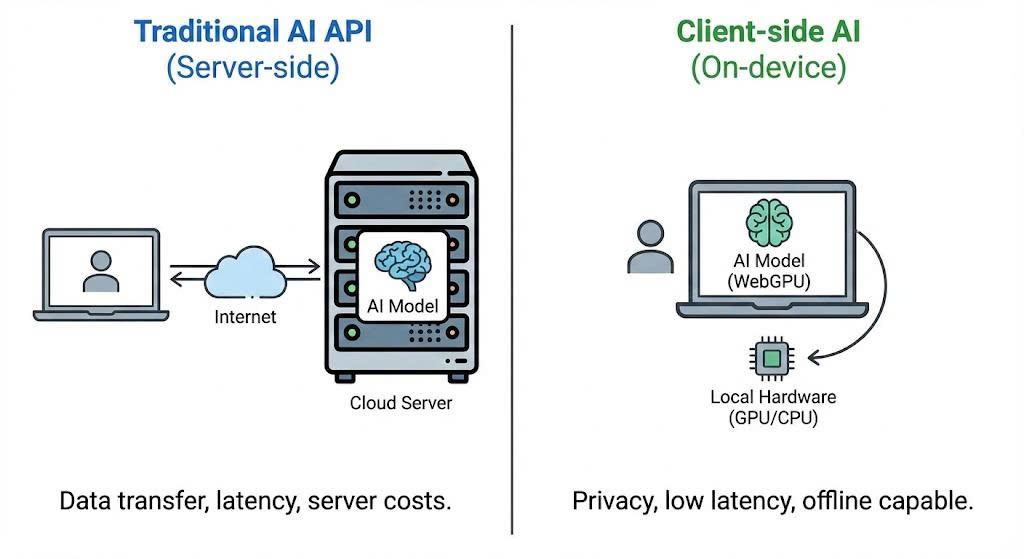
Difference between Server-side Inference and Client-side Inference
More: Google MediaPipe LLM Inference
Prerequisites
Browser & Hardware
Note: Since WebGPU is a relatively new technology, ensure your environment meets the requirements to avoid browser crashes due to VRAM shortage.
I. Supported Browsers
- Google Chrome / Edge: Version 113 or higher (WebGPU enabled by default).
- Firefox/Safari: Currently experimental (requires manual flag enabling).
II. Recommended Hardware (For Gemma 2B/Similar Models)
- GPU: WebGPU compatible (NVIDIA GTX 1060 or higher, Apple Silicon M1/M2/M3, or equivalent AMD Radeon).
- VRAM: Minimum 4GB VRAM for smooth model loading.
- RAM: Minimum 8GB System RAM.
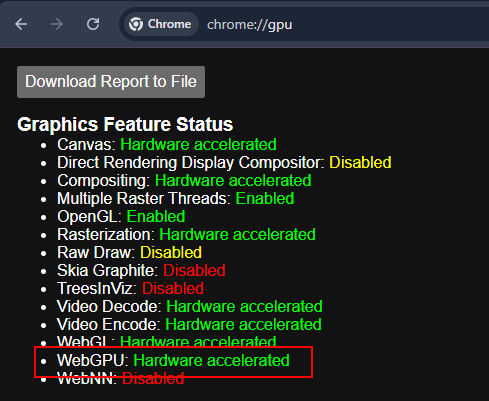
Check WebGPU status: Hardware acceleration must be enabled.
Implementation
In this guide, we will use Google’s MediaPipe LLM Inference API to run the gemma-3n-E2B-it-litert-lm model. This model is lightweight enough (just over 3GB) to run on the web while remaining smart enough for basic tasks.
We will create a simple HTML/JS project. No complex backend setup is required.
1. Folder Structure and Model Download
nquangit@local-dev:~/ai-projects/gemma-web$ tree
.
├── index.html
├── gemma-3n-E2B-it-int4-Web.litertlm
└── index.js
0 directories, 3 files
nquangit@local-dev:~/ai-projects/gemma-web$
You can find and download the model file gemma-3n-E2B-it-int4-Web.litertlm from Hugging Face - Google.
You need to log in to Hugging Face and request access to the model from Google before you can download it. Additionally, you can use any other LitERT-LM model with a similar format.
2. HTML UI
You can use NPM or a CDN. For demonstration simplicity, I will use the CDN in index.html.
I also added some CSS to make the interface look cleaner and more modern.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>LLM Inference Web Demo</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #1a1a2e 0%, #16213e 50%, #0f3460 100%);
min-height: 100vh;
padding: 20px;
color: #e4e4e4;
}
.container {
max-width: 900px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
header {
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
header h1 {
font-size: 2.2rem;
font-weight: 600;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #00d4ff, #7b2cbf);
-webkit-background-clip: text;
-webkit-text-fill-color: transparent;
background-clip: text;
margin-bottom: 8px;
}
header p {
color: #94a3b8;
font-size: 0.95rem;
}
.chat-container {
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.05);
backdrop-filter: blur(10px);
border-radius: 16px;
border: 1px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
padding: 24px;
box-shadow: 0 8px 32px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
}
.section {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.section:last-child {
margin-bottom: 0;
}
label {
display: block;
font-size: 0.85rem;
font-weight: 500;
color: #94a3b8;
margin-bottom: 8px;
text-transform: uppercase;
letter-spacing: 0.5px;
}
textarea {
width: 100%;
height: 180px;
padding: 16px;
border: 1px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
border-radius: 12px;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
color: #e4e4e4;
font-family: 'Consolas', 'Monaco', monospace;
font-size: 0.95rem;
line-height: 1.6;
resize: vertical;
transition: border-color 0.3s ease, box-shadow 0.3s ease;
}
textarea:focus {
outline: none;
border-color: #00d4ff;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px rgba(0, 212, 255, 0.1);
}
textarea::placeholder {
color: #64748b;
}
#output {
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
min-height: 200px;
}
.button-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
margin: 24px 0;
}
#submit {
padding: 14px 40px;
font-size: 1rem;
font-weight: 600;
color: white;
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #00d4ff 0%, #7b2cbf 100%);
border: none;
border-radius: 50px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
box-shadow: 0 4px 15px rgba(0, 212, 255, 0.3);
}
#submit:hover:not(:disabled) {
transform: translateY(-2px);
box-shadow: 0 6px 20px rgba(0, 212, 255, 0.4);
}
#submit:active:not(:disabled) {
transform: translateY(0);
}
#submit:disabled {
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #4a5568 0%, #2d3748 100%);
cursor: not-allowed;
box-shadow: none;
}
#submit.loading {
position: relative;
color: transparent;
}
#submit.loading::after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -10px;
margin-top: -10px;
border: 3px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3);
border-radius: 50%;
border-top-color: white;
animation: spin 1s linear infinite;
}
@keyframes spin {
to { transform: rotate(360deg); }
}
.status-bar {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
gap: 8px;
padding: 12px;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
border-radius: 8px;
margin-top: 16px;
}
.status-indicator {
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #64748b;
}
.status-indicator.loading {
background: #fbbf24;
animation: pulse 1.5s infinite;
}
.status-indicator.ready {
background: #22c55e;
}
@keyframes pulse {
0%, 100% { opacity: 1; }
50% { opacity: 0.5; }
}
#status-text {
font-size: 0.85rem;
color: #94a3b8;
}
footer {
text-align: center;
margin-top: 24px;
color: #64748b;
font-size: 0.8rem;
}
footer a {
color: #00d4ff;
text-decoration: none;
}
footer a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
@media (max-width: 600px) {
body {
padding: 12px;
}
header h1 {
font-size: 1.6rem;
}
.chat-container {
padding: 16px;
}
textarea {
height: 140px;
font-size: 0.9rem;
}
#submit {
width: 100%;
padding: 16px;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<header>
<h1>🤖 AI Chat Demo</h1>
<p>Powered by MediaPipe LLM Inference</p>
</header>
<div class="chat-container">
<div class="section">
<label for="input">Your Message</label>
<textarea id="input" placeholder="Type your message here..."></textarea>
</div>
<div class="button-container">
<button id="submit" disabled>Get Response</button>
</div>
<div class="section">
<label for="output">AI Response</label>
<textarea id="output" readonly placeholder="Response will appear here..."></textarea>
</div>
<div class="status-bar">
<div id="status-indicator" class="status-indicator loading"></div>
<span id="status-text">Loading model...</span>
</div>
</div>
<footer>
<p>Built with <a href="[https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/genai/llm_inference/web_js](https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/genai/llm_inference/web_js)" target="_blank">MediaPipe GenAI</a></p>
</footer>
</div>
<script type="module" src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
3. JavaScript Logic
We need to load the FilesetResolver (WASM binaries) and initialize the LlmInference engine.
We also need to handle the event when the user clicks the send button and display the returned result.
Note: The Gemma model
gemma-3n-E2B-it-litert-lmis approximately 3.4GB. The initial load time will depend on your network speed.
// You can refer to this file from [Google AI Edge](https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samples/blob/main/examples/llm_inference/js/index.js)
// index.js
import {FilesetResolver, LlmInference} from '[https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@mediapipe/tasks-genai](https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@mediapipe/tasks-genai)';
const input = document.getElementById('input');
const output = document.getElementById('output');
const submit = document.getElementById('submit');
const statusIndicator = document.getElementById('status-indicator');
const statusText = document.getElementById('status-text');
const modelFileName = 'gemma-3n-E2B-it-int4-Web.litertlm'; /* Update the file name */
/**
* Update the status bar UI
*/
function updateStatus(state, message) {
statusIndicator.className = 'status-indicator ' + state;
statusText.textContent = message;
}
/**
* Display newly generated partial results to the output text box.
*/
function displayPartialResults(partialResults, complete) {
output.textContent += partialResults;
// Auto-scroll to bottom
output.scrollTop = output.scrollHeight;
if (complete) {
if (!output.textContent) {
output.textContent = 'Result is empty';
}
submit.disabled = false;
submit.classList.remove('loading');
submit.textContent = 'Get Response';
updateStatus('ready', 'Ready');
}
}
/**
* Main function to run LLM Inference.
*/
async function runDemo() {
const genaiFileset = await FilesetResolver.forGenAiTasks(
'[https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@mediapipe/tasks-genai/wasm](https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@mediapipe/tasks-genai/wasm)');
let llmInference;
submit.onclick = () => {
if (!input.value.trim()) {
input.focus();
return;
}
output.textContent = '';
submit.disabled = true;
submit.classList.add('loading');
submit.textContent = '';
updateStatus('loading', 'Generating response...');
llmInference.generateResponse(input.value, displayPartialResults);
};
// Allow Ctrl+Enter to submit
input.addEventListener('keydown', (e) => {
if (e.ctrlKey && e.key === 'Enter' && !submit.disabled) {
submit.click();
}
});
updateStatus('loading', 'Loading model...');
submit.textContent = 'Loading...';
LlmInference
.createFromOptions(genaiFileset, {
baseOptions: {modelAssetPath: modelFileName},
// maxTokens: 512, // The maximum number of tokens (input tokens + output
// // tokens) the model handles.
// randomSeed: 1, // The random seed used during text generation.
// topK: 1, // The number of tokens the model considers at each step of
// // generation. Limits predictions to the top k most-probable
// // tokens. Setting randomSeed is required for this to make
// // effects.
// temperature:
// 1.0, // The amount of randomness introduced during generation.
// // Setting randomSeed is required for this to make effects.
})
.then(llm => {
llmInference = llm;
submit.disabled = false;
submit.textContent = 'Get Response';
updateStatus('ready', 'Model loaded • Ready');
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('Failed to initialize:', error);
updateStatus('', 'Failed to load model');
submit.textContent = 'Error';
alert('Failed to initialize the task.');
});
}
runDemo();
Testing
After coding, you need to run the index.html file via an HTTP Server (WebGPU requires a Secure Context or localhost).
Use any HTTP server or the Live Server extension in VSCode.
Open your browser and test it out:
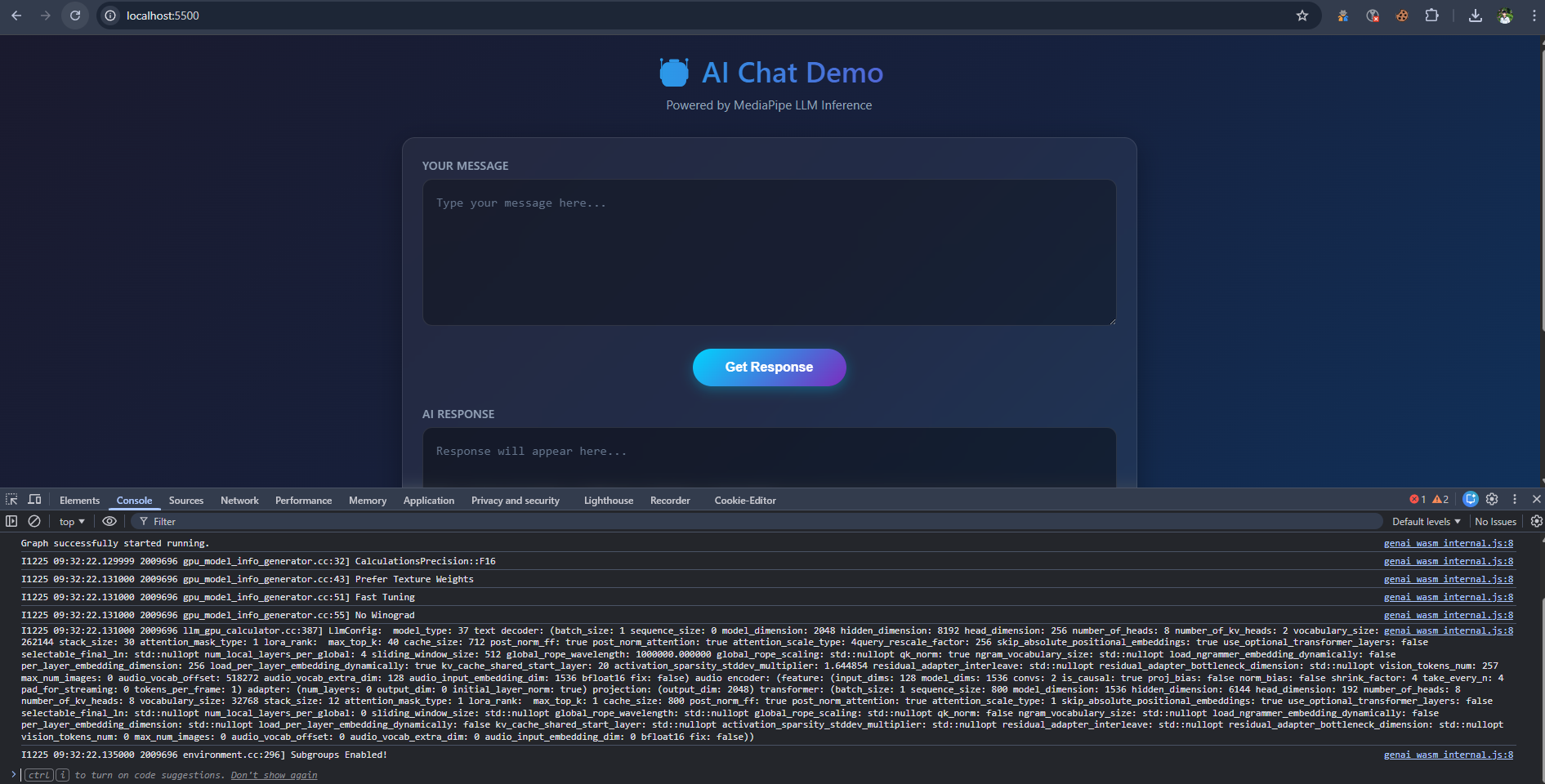
Initialization Console Log
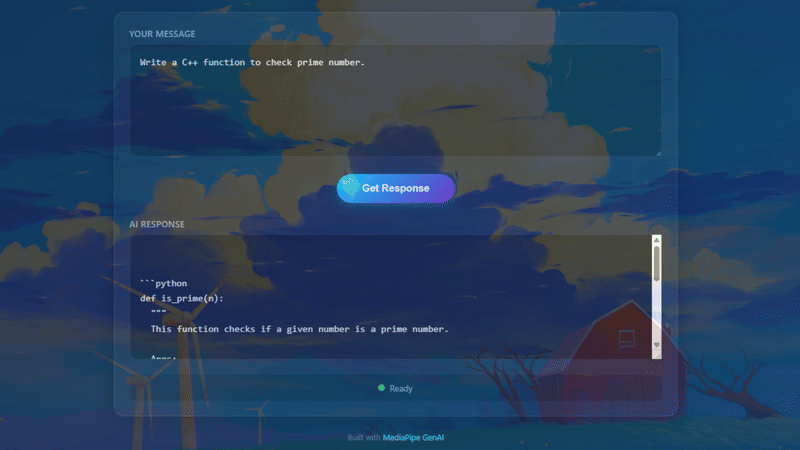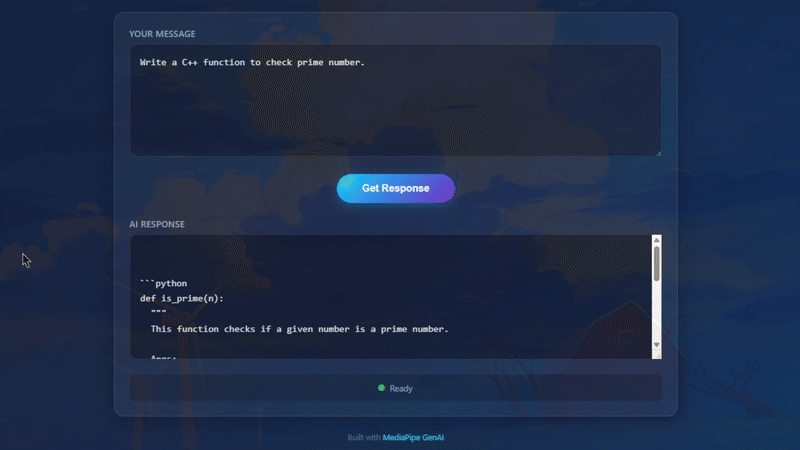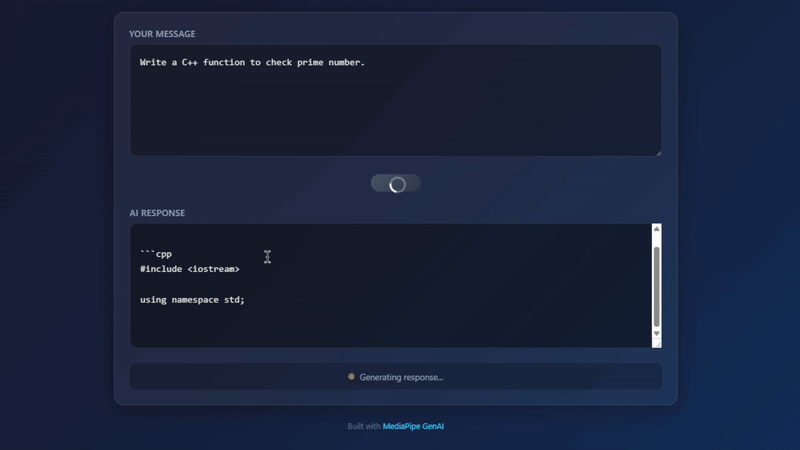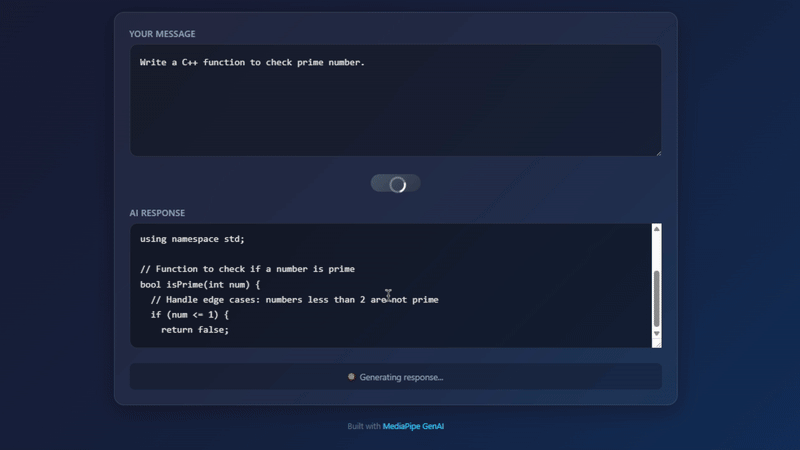
Actual result running on Chrome
Let’s try asking a coding question:
User: Write a Python function to check prime number.
AI Response:
def is_prime(n):
"""
This function checks if a given number is a prime number.
Args:
n: The number to check.
Returns:
True if the number is prime, False otherwise.
"""
if n <= 1:
return False
for i in range(2, int(n**0.5) + 1):
if n % i == 0:
return False
return True
If you see the text rendering speed is comparable to typing speed, congratulations, WebGPU is working well on your machine!
Note: The current implementation does not persist the model (e.g., using IndexedDB). Therefore, reloading the page will trigger a re-download of the model from scratch (although on localhost, the transfer speed will be very fast).
Conclusion
Running LLMs directly in the browser opens up massive potential for Web 3.0 and privacy-focused applications.
- Pros: Secure, zero server operation costs, offline capable.
- Cons: Heavy initial model download (GBs), dependent on user hardware.
With optimizations from Google MediaPipe and the widespread adoption of WebGPU, these barriers are gradually being removed.
See you in the next posts about model optimization with WebLLM!


Leave a comment